The term superfood is commonly used in health and fitness to describe nutrient-rich foods. Common examples include leafy vegetables, berries, and nuts, which are known for their high levels of vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. Such foods enhance general health when added to a healthy diet.
Cockroach Milk A Surprising New Contender
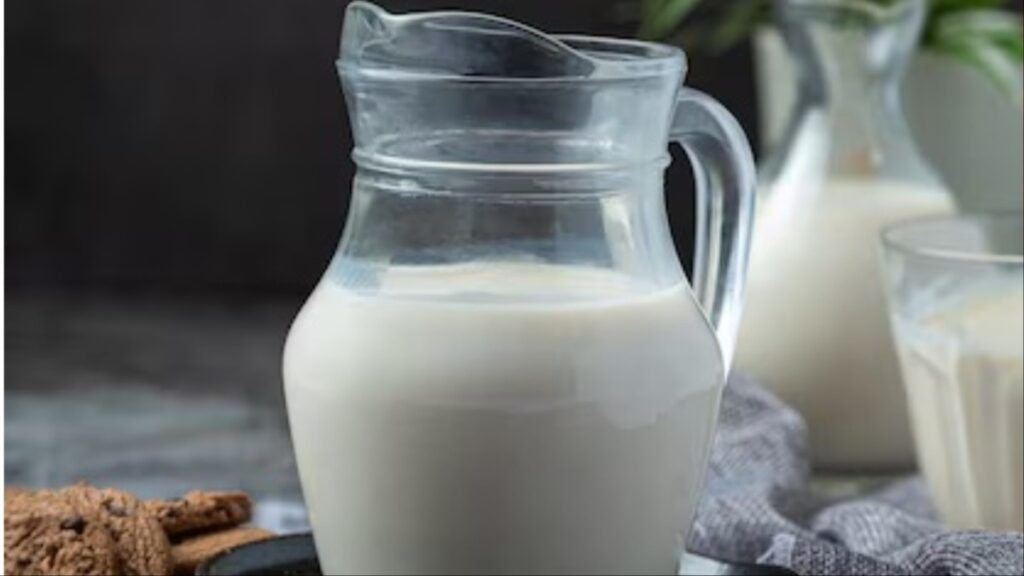
Recent scientific research has found an unexpected new addition to the superfood group cockroach milk. It may sound bizarre, but scientists have discovered that milk from the Pacific beetle cockroach (Diploptera punctata) is potentially three times more nutritious than cow’s milk.
This cockroach species produces a nutrient-rich milky substabce to nourish its young ones. Scientists believe that this liquid contains proteins, fat, and sugar, thus is one of the most nutrition-dense naturally occurring substances identified until now. Given its nutrition content, researchers believe that it could play a role in future food technology.
What Does Research Say?
A 2016 study, published in the Journal of the International Union of Crystallography, investigated this peculiar milk-like substance. Scientists discovered that when young cockroaches ingested it, the material crystallized within their stomachs.
According to a report in The Independent, this milk has three times the calories of buffalo milk, which was once thought to be the most calorie-dense mammalian milk. It is also full of proteins, amino acids, and good sugars, all of which are vital for cell repair and growth.
Can Humans Eat Cockroach Milk?
Despite its remarkable nutritional profile, cockroach milk is not yet attainable for human consumption. The most significant hurdle lies in its production, as extracting milk from cockroaches is an elaborate and labor-intensive process.
Like all superfoods, cockroach milk should be viewed as a supplement. While further research is needed, this research could open the way for sustainable and nutritious food options in the future.