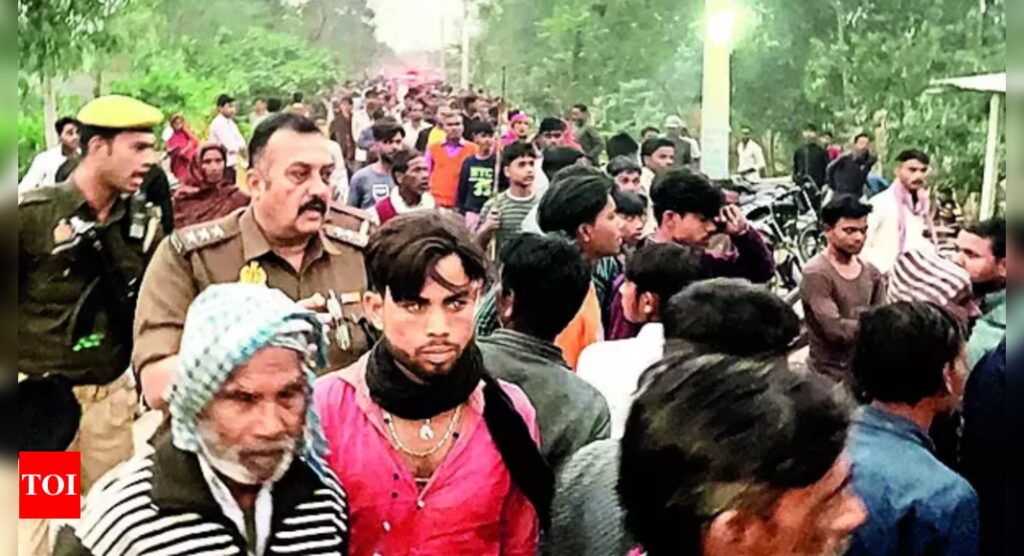
PILIBHIT: The foot-and-mouth disease (FMD) has affected around 60% milch cattle in Pilibhit district. Besides, stray cattle are also at the risk of being infected with the highly contagious disease. In order to control the disease, the animal husbandry department has arranged over 3 lakh vaccines, officials said. As per the official figures, the dairy owners and agricultural farmers in Pilibhit district are in possession of over 3.5 lakh cows and buffaloes.
According to veterinary scientists, the infection can be transmitted to humans by consuming raw or pasteurised milk of the infected cattle.
BR Singh, head of epidemiology division at Bareilly-based Indian Institute of Veterinary Research, said, “The infection can easily be transmitted to those milking the cattle as they come in direct contact with the infected animals. Raw or pasteurised milk of the infected cattle could also be a potential way of infection getting transmitted to humans although it is not fatal.”
“The FMD is an air borne viral disease which can transmit to other animals by licking. The vaccination will be administered to those cattle which have not been infected yet. The ones impacted by the virus may take a fortnight to recover with proper medication. The milk producing capacity of the affected cattle gradually reduces to zero”, said Dr Laxmi Prasad, deputy chief veterinary officer at Pilibhit.
“Veterinarians of 16 hospitals in the district have been directed to participate in the vaccination drive which is being conducted at the hospital campuses apart from door-to-door visits to dairy farms. Private vaccinators and para-veterinary workers have also been deployed to provide assistance”, said Dr Arvind Garg, chief veterinary officer.
Meanwhile, dairy keepers in Pilibhit city, said, “Had the animal husbandry department initiated the vaccination drive in time, our cattle could have been saved.” They also claimed that “since the govt veterinary hospitals are not providing proper treatment to the affected cattle, they were forced to visit private veterinarians who charge hefty amounts.
According to veterinary scientists, the infection can be transmitted to humans by consuming raw or pasteurised milk of the infected cattle.
BR Singh, head of epidemiology division at Bareilly-based Indian Institute of Veterinary Research, said, “The infection can easily be transmitted to those milking the cattle as they come in direct contact with the infected animals. Raw or pasteurised milk of the infected cattle could also be a potential way of infection getting transmitted to humans although it is not fatal.”
“The FMD is an air borne viral disease which can transmit to other animals by licking. The vaccination will be administered to those cattle which have not been infected yet. The ones impacted by the virus may take a fortnight to recover with proper medication. The milk producing capacity of the affected cattle gradually reduces to zero”, said Dr Laxmi Prasad, deputy chief veterinary officer at Pilibhit.
“Veterinarians of 16 hospitals in the district have been directed to participate in the vaccination drive which is being conducted at the hospital campuses apart from door-to-door visits to dairy farms. Private vaccinators and para-veterinary workers have also been deployed to provide assistance”, said Dr Arvind Garg, chief veterinary officer.
Meanwhile, dairy keepers in Pilibhit city, said, “Had the animal husbandry department initiated the vaccination drive in time, our cattle could have been saved.” They also claimed that “since the govt veterinary hospitals are not providing proper treatment to the affected cattle, they were forced to visit private veterinarians who charge hefty amounts.