)
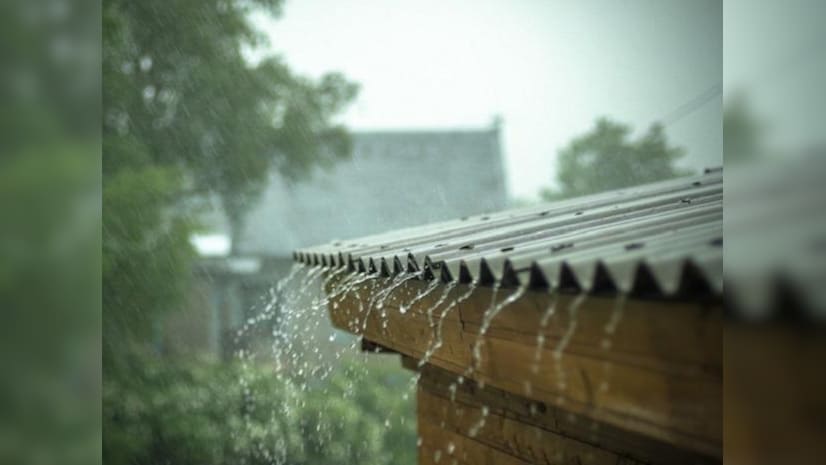
The monsoon generally begins in June and starts to retreat by Sept. 17.
India’s monsoon rains are likely to be prolonged into late September this year due to the development of a low-pressure system in the middle of the month, two weather department officials told Reuters.
Above-normal rainfall due to the delayed withdrawal of the monsoon could damage India’s summer-sown crops like rice, cotton, soybean, corn, and pulses, which are typically harvested from mid-September.
The crop damage could lead to food inflation, but the rains may also result in higher soil moisture, benefiting the planting of winter-sown crops such as wheat, rapeseed, and chickpea.
“There is an increased probability of a low-pressure system developing in the third week of September, which could delay the withdrawal of the monsoon,” said a senior official of the India Meteorological Department, who sought anonymity as the matter is sensitive.
India, the world’s second-largest producer of wheat, sugar, and rice, has imposed various curbs on the export of these farm commodities, and any losses due to excessive rainfall could prompt New Delhi to extend those curbs.
The monsoon generally begins in June and starts to retreat by Sept. 17 from northwestern parts of the country, ending across the country by mid-October.
The lifeblood of a nearly $3.5-trillion economy, the annual monsoon brings almost 70 per cent of the rain India needs to water farms and replenish reservoirs and aquifers. Without irrigation, nearly half the farmland in the country depends on the rains that usually run from June to September.
Monsoon rainfall in September and October could be influenced by La Nina weather conditions, which are likely to develop from the next month, said another IMD official.
In the past, when La Nina develops during the second half of the monsoon season, it has led to a delayed monsoon withdrawal, said the official, adding that “this year, we could see a similar pattern”.
The two sources shared their assessment ahead of the IMD’s monthly forecast for September rainfall and monsoon withdrawal, which is scheduled for this weekend.
India has received 7 per cent more rainfall than average since the monsoon season began on June 1. However, some states have experienced as much as 66 per cent more rainfall than average, leading to flooding.
Heavy rains during the third and fourth weeks of September and early October could affect early sown crops that are nearing harvest, said Ashwini Bansod, vice president of commodities research at Phillip Capital India.
(Only the headline and picture of this report may have been reworked by the Business Standard staff; the rest of the content is auto-generated from a syndicated feed.)
First Published: Aug 29 2024 | 7:17 PM IST