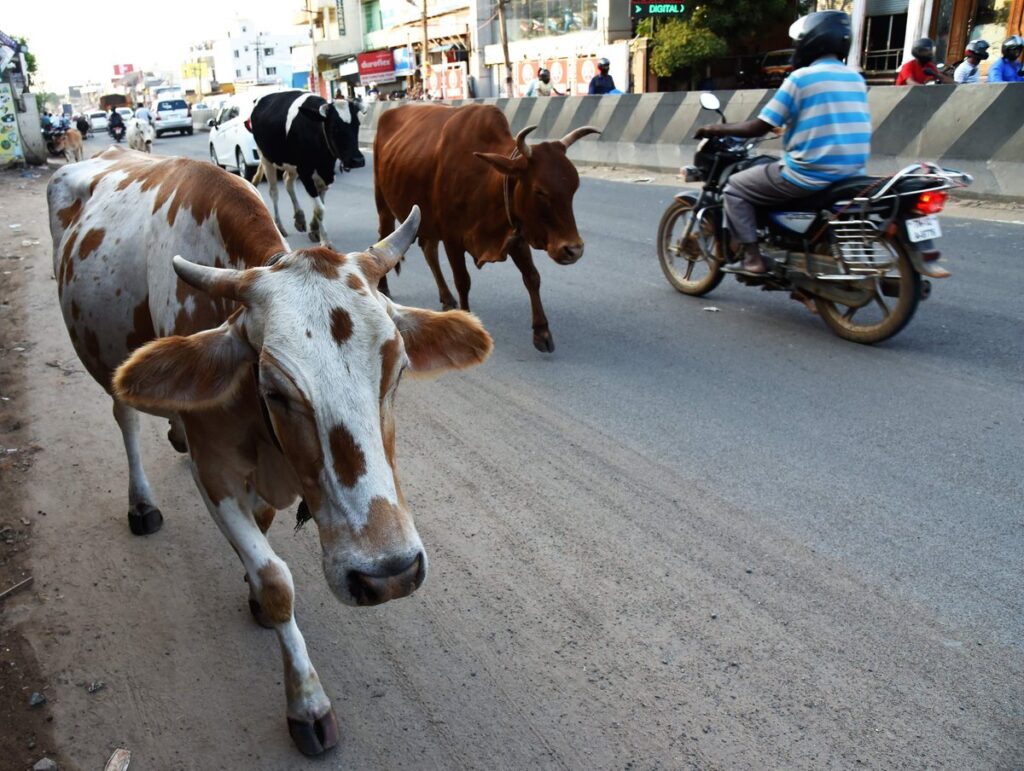
Milk supply safe
Experts are worried about the increasing number of mammals infected by the current H5N1 strain of Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza (HPAI) and whether it is actually spreading between them.
“Initial testing has not found changes to the virus that would make it more transmissible to humans,” the US Department of Agriculture, the CDC, and the Food and Drug Administration said in a joint statement last week.
The strain appears to have been introduced by wild birds but spread between cows hasn’t been ruled out, the statement added.
The Texas health department said the cattle infections do not present a concern for the commercial milk supply, as dairies are required to destroy milk from sick cows. Pasteurization also kills the virus.
The findings marked the first time ever that HPAI has been detected in dairy cattle, according to the American Veterinary Medical Association (AVMA). Earlier in March, Minnesota reported bird flu cases among goats.
Ongoing outbreak
The affected cows were primarily older animals that showed decreased lactation and low appetite, “with little to no associated mortality reported,” added the AVMA. Dead wild birds were generally found nearby.
A nine-year-old boy died from the virus in Cambodia in February, adding to the three deaths there in 2023 — though the bird flu spreading in Europe and North America appears to cause milder infections, said Moncla.
Bird flu has killed tens of thousands of marine mammals since spreading in South America, according to the Scientific Committee on Antarctic Research.
British seabird populations are suffering “widespread and extensive declines” according to a recent impact assessment.
The disease has hit European farms hard too, with French authorities raising the risk level to “maximum” in December, and Czech officials reporting in February they had culled 140,000 birds in 2024 alone.